Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Oct 13, 2025

Personalized Nutrition Ecosystem
In recent years, “personalized nutrition” has moved from buzzword to strategic imperative across the food, beverage, and nutraceutical industries. Consumers are increasingly rejecting a one-size-fits-all approach to diet and health, demanding solutions tailored to their unique genetics, microbiomes, metabolic profiles, lifestyle patterns, and even taste preferences. Within this paradigm shift, the role of flavor is often underestimated—but in fact, flavor is a critical enabler. Flavor bridges the gap between “healthy but bland” and “delicious and bespoke.” For a manufacturer of food and beverage flavors, understanding and harnessing this role is a powerful competitive advantage.
In this deep-dive, we will explore:
Our goal is to equip you with authoritative, persuasive content suitable for a corporate blog—optimized for readability and with clear citations to bolster trust.
Personalized nutrition (also referred to as precision nutrition, individualized nutrition, or nutrigenomics/nutrigenetics) aims to tailor dietary recommendations or food products to the individual, rather than broad population-level guidelines. This tailoring can integrate a variety of personal data inputs:
In its simplest form, personalization might let a consumer choose a flavor variant or color. On the more advanced end, it could involve dynamic meal recommendations based on continuous glucose monitoring or AI‐driven analysis of personal health trends. www.diana-food.com+1
According to Glanbia Nutritionals, the global personalized nutrition market is forecast to grow from about $8.3 billion in 2020 to $21.4 billion by 2028 (CAGR ~13.4 %) Glanbia. Grand View Research similarly highlights how AI, genomics, and digital health platforms are driving innovation in the personalized nutrition and supplement segments Grand View Research.
Several interconnected trends are fueling the rise of personalized nutrition:
Given these trends, food and beverage companies that can embed personalization—especially via flavor—into their propositions are better positioned to differentiate and retain consumer loyalty.
Flavor is not just a “nice-to-have.” In many ways, it is the linchpin that makes personalized nutrition both practical and palatable.
A tailored nutritional formula—whether a protein shake, micro-nutrient drink, or functional snack—is only effective if the consumer will actually consume it over time. If the product tastes bland, off-putting, or mismatched to a user’s palate, adherence drops dramatically.
Scientific studies confirm that taste receptors can influence dietary choices, which in turn shape nutritional status and health outcomes. PMC+1 A recent review highlights the role of flavor in influencing eating decisions, metabolic responses, and overall well-being. PMC
Thus, in a personalized nutrition regimen, flavor plays a twofold role:
Just as people prefer certain scents, music, or aesthetics, they often have strong flavor identities: “I like citrus-forward,” “I prefer mild herbal,” “I don’t like mint,” etc. Incorporating flavor preferences into personalization helps products resonate psychologically.
This “flavor identity” dimension reinforces the notion that the product is uniquely “for me.” It helps brands shift from functional to emotional connection. Industry commentary has begun to note that custom flavor development is a rising trend, particularly for health-forward formats. Mother Murphys
Modern flavor design doesn’t just mask bitterness or off-notes—it can incorporate functional ingredients (botanicals, adaptogens, nootropics) and support product claims (e.g., “calming herbal berry,” “metabolic citrus”) without compromising sensory quality. The emerging class of functional flavors allows flavor systems to carry secondary benefit messaging implicitly. fychemgroup.com
Flavors can modulate perceptions of sweetness, saltiness, or umami such that you use less sugar, sodium, or additives while maintaining palatability. Moreover, flavor‐nutrient interactions can influence digestive responses (e.g., aroma triggers cephalic phase responses).
Advanced flavor systems—even ones using taste receptor assays or receptor-based screening—can help tailor the sensory effect precisely. (Senomyx is an example of a company that developed taste receptor–based assays to design flavor enhancers) Wikipedia
In summary, flavor is not superficial—it’s deeply woven into consumer behavior, sensory physiology, and the business model of personalized nutrition.
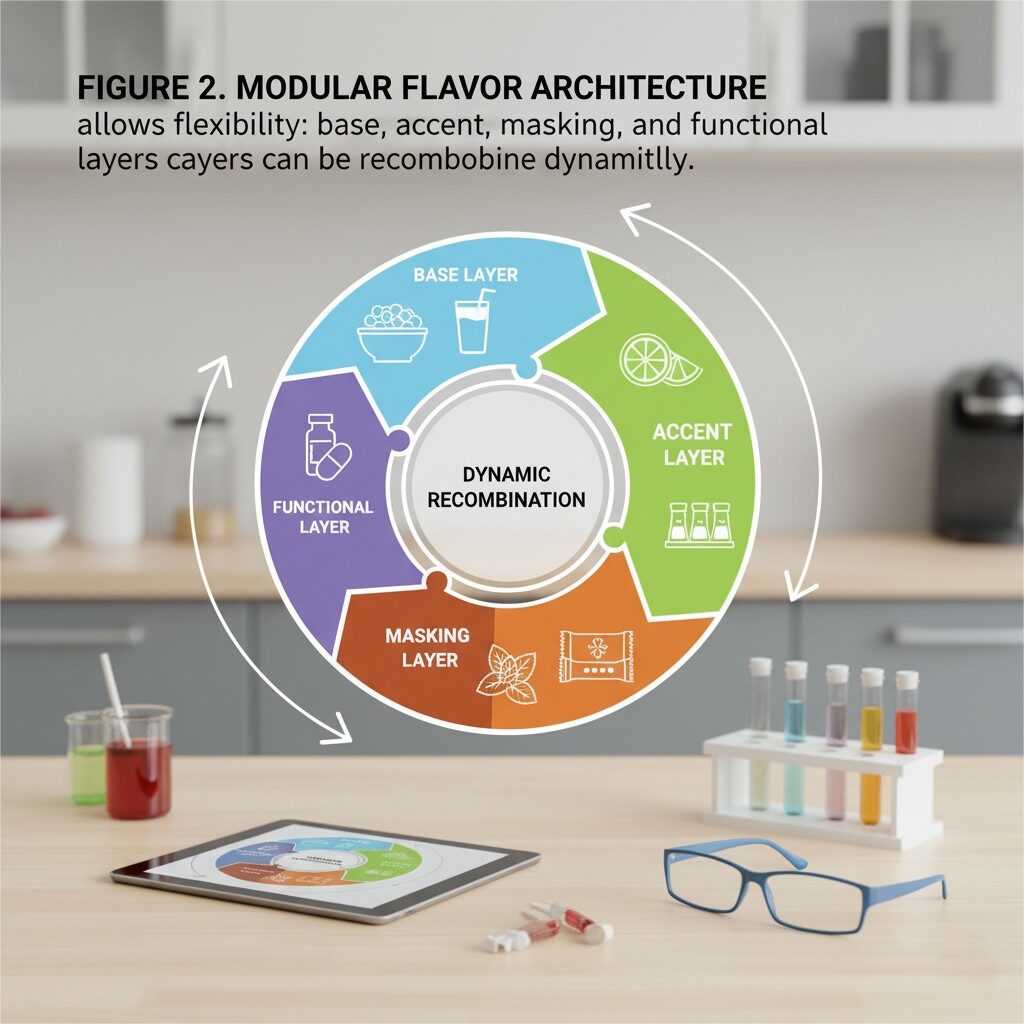
Modular Flavor Architecture
Bridging science and commerce, flavor houses and formulators must think creatively and precisely. Below are key technical strategies and best practices for integrating flavor into personalized solutions.
To create a flavor “palette” aligned with personalization, begin with flavor mapping:
This allows creating a modular flavor system that can be recombined dynamically.
Rather than designing fixed flavors, consider building modular flavor building blocks (e.g., base, accent, finishing, masking layers). This enables combinatorial flexibility:
This system lets customization engines (e.g., via web or app) mix and match modules to generate unique flavor blends per consumer.
Personalized formulas often contain bioactives, vitamins, polyphenols, or plant extracts that carry bitterness or astringency. Effective masking is critical:
Optimizing masking often requires iterative sensory testing and analytic tools (GC-MS, GC-olfactometry, sensory panels).
One hallmark of personalized nutrition platforms is dynamic adjustment. Through feedback (consumer reviews, preference rating, metabolic data), flavor profiles can be updated post-launch:
This dynamic approach can boost retention and loyalty.
Recent advances combine AI, machine learning, and computational gastronomy to accelerate flavor development and personalization:
By integrating flavor design AI with nutrition personalization engines, the time to consumer-ready bespoke flavors can shrink dramatically.
Flavor performance in personalized nutrition must account for:
Careful formulation ensures that the promise of bespoke flavor meets the realities of shelf life, cost, and regulatory safety.

AI Flavor Feedback Loop
Flavor-enabled personalization can span a broad range of product categories. Below are illustrative use cases and considerations.
Why it’s a key entry point: liquid formats are modular, relatively easy to flavor, and often consumed daily—providing maximum interaction.
Hartman Group has observed that 60 % of consumers report adding or increasing protein in their diet, indicating strong opportunity for personalized beverage platforms.
Technical considerations:
Personalization in solid formats poses challenges but offers differentiation:
Flavor systems must handle dry processing, shelf stability, and uniform distribution.
At a more premium end, culinary personalization can leverage flavor modules in meal kits, restaurants, or custom-ordered dishes:
Research in gastronomy emphasizes that each transformation stage of food affects the release of flavor and aroma—all relevant in personalized formulations.
Holistic personalization might consider pairing flavor with color, texture, aroma, or even sound:
Flavor thus becomes part of a broader personalized consumer experience.
To support flavor-enabled personalized nutrition, manufacturers and brands must think beyond formula—it’s an ecosystem.
Flavor houses should integrate with brand partners’ personalization engines:
Close coupling between flavor design and digital analytics is crucial.
Many personalized nutrition services adopt subscription models. Flavor can be a point of differentiation:
Modular flavor architecture helps reduce costs and speed deployment.
Rather than merely selling flavors, forward-looking flavor houses may enter co-development with F&B brands:
This closer alignment strengthens client ties and positions flavor houses as innovation partners.
Flavor suppliers and brands must navigate regulatory challenges:
Positioning flavor systems to align with clients’ claim strategies is a value-add.
Even as opportunities abound, implementing flavor in personalized nutrition is not trivial. Here are key challenges and mitigations.
Challenge: Designing and managing countless flavor permutations can overwhelm manufacturing, supply chain, and quality control.
Mitigation:
Challenge: Flavors degrade over time; modulization may lead to instability.
Mitigation:
Challenge: Some consumers may dislike their assigned flavor, reducing adherence.
Mitigation:
Challenge: Bespoke flavor must not create prohibitive cost burden.
Mitigation:
Challenge: Flavor recipes risk being reverse-engineered or commoditized.
Mitigation:
Looking ahead, flavor-enabled personalized nutrition is likely to evolve along several exciting vectors.
In the near future, consumers may receive flavor-adapted products based on real-time biometrics (e.g., glucose levels, heart rate). Flavor systems may adapt in “just-in-time” fashion.
Flavor design is entering a new era: AI and generative models can propose novel flavor compounds or combinations tailored to individual sensory response curves. This co-optimization (flavor + bioactivity) is an emerging frontier. Ift Online Library+1
As personalized nutrition increasingly relies on microbiome and metabolomic data, flavors may be tuned to modulate metabolic pathways or microbial signaling—e.g., flavors that promote satiety or modulate gut fermentation.
Flavor systems may shift subtly over time to promote behavioral goals (e.g., gradually reducing sugar sensation strength). Flavor can become a behavioral nudge tool.
Beyond flavor, the packaging, texture, color, and aroma may all be personalized in tandem—creating a unified, immersive experience.

Future of Flavor Personalization
Below are three illustrative diagrams to contextualize how flavor fits into personalized nutrition ecosystems.
| Figure | Title | Description |
| Figure 1 | Personalization Input-Output Model | Shows how inputs (genomics, microbiome, biomarkers, preferences) feed into a personalization engine, which outputs a formulation + flavor recipe. |
| Figure 2 | Flavor Module Architecture | Depicts base, accent, masking, and functional modules combining to form a final flavor blend. |
| Figure 3 | Feedback Loop & Flavor Adjustment | Visualizes iterative process where consumer feedback and biomarker data refine flavor recommendations over time. |
To summarize:
From your vantage as a manufacturer of food and beverage flavors, the opportunity is clear: you can move from being a commodity supplier to a strategic partner in your clients’ personalized nutrition journeys.
We encourage you to:
Are you exploring personalized nutrition solutions or looking to integrate bespoke flavor systems into your formulations? We welcome technical exchange, collaborative R&D, and free sample requests. Contact us today to co-create the next generation of personalized food and beverage products.
📩 [info@cuiguai.com]
📞 [+86 189 2926 7983]
🌐 Explore more at 【www.cuiguai.cn】
Copyright © 2025 Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.