Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Oct 30, 2025

Automated Flavor Production Infographic
In the highly competitive food & beverage flavours industry, manufacturers face mounting pressures: tighter margins, rising raw-material costs, increasing regulatory scrutiny, demand for consistency and traceability, and the need to launch new flavour systems faster than ever. For flavour houses and aroma system suppliers (like your company), the ability to apply flavours precisely and efficiently across all production scales is a strategic differentiator.
Automation in flavour application is no longer an optional luxury—it is becoming a core capability. From metered dosing of aroma concentrates, to closed-loop monitoring of flavour injection, to full integration with production lines and ERP systems, automation enables your company and your clients to deliver consistent flavour quality, reduce waste, improve traceability, and respond swiftly to market demands.
This blog post provides a technical, authoritative, and well-structured guide to automation in flavour application—written with manufacturing professionals in mind and optimized for Google indexing. We will cover:
By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive framework for how automation in flavour application can elevate your manufacturing operations—and what you need to do to deliver this value to your clients and your brand.
For flavour manufacturers supplying food & beverage producers, flavour application often involves manual steps: measuring concentrates, hand-adjusting injection pumps, adjusting for variability in batches, tuning settings, verifying sensory output. Manual operations introduce variability, error risk, slower change-over, higher waste, and slower response to new flavour systems.
Manual application also makes consistency across batches and sites difficult, complicates traceability, and reduces scalability. As one article notes: “Automation can help companies achieve better results with fewer workers… automated systems can take care of many of the inconsistencies and human errors that cause problems for food companies.”
Consistency of flavour profile – Consumers expect the same taste every time; for your B2B clients (food & beverage brands), deviation in flavour is unacceptable. Automation improves precision and repeatability.
Efficiency / throughput – Automated systems enable higher speed, less downtime, faster change-overs for flavour variants, and scalability of flavour application operations.
Traceability & quality control – Regulatory pressures (e.g., FDA, HACCP) and brand-integrity demands mean that every flavour batch must be traceable; automation helps capture data, sensor logs, batch-IDs, and integration with production systems.
Waste reduction and cost control – Precise dosing reduces over-use of expensive flavour concentrates, minimises rework/scrap, lowers labour cost, and promotes sustainability.
Flexibility and innovation speed – Automated flavour application allows quicker introduction of new flavours, easier change-overs, more agile response to consumer trends and market changes. As the food industry moves toward “Smart Manufacturing”, automation is required to adapt quickly.
Given these imperatives, your company—as a professional manufacturer of food & beverage flavours—is well placed to champion automated flavour application systems, deliver aroma modules configured for automation, and support clients in deploying automated flavour lines. The rest of this article explores how.
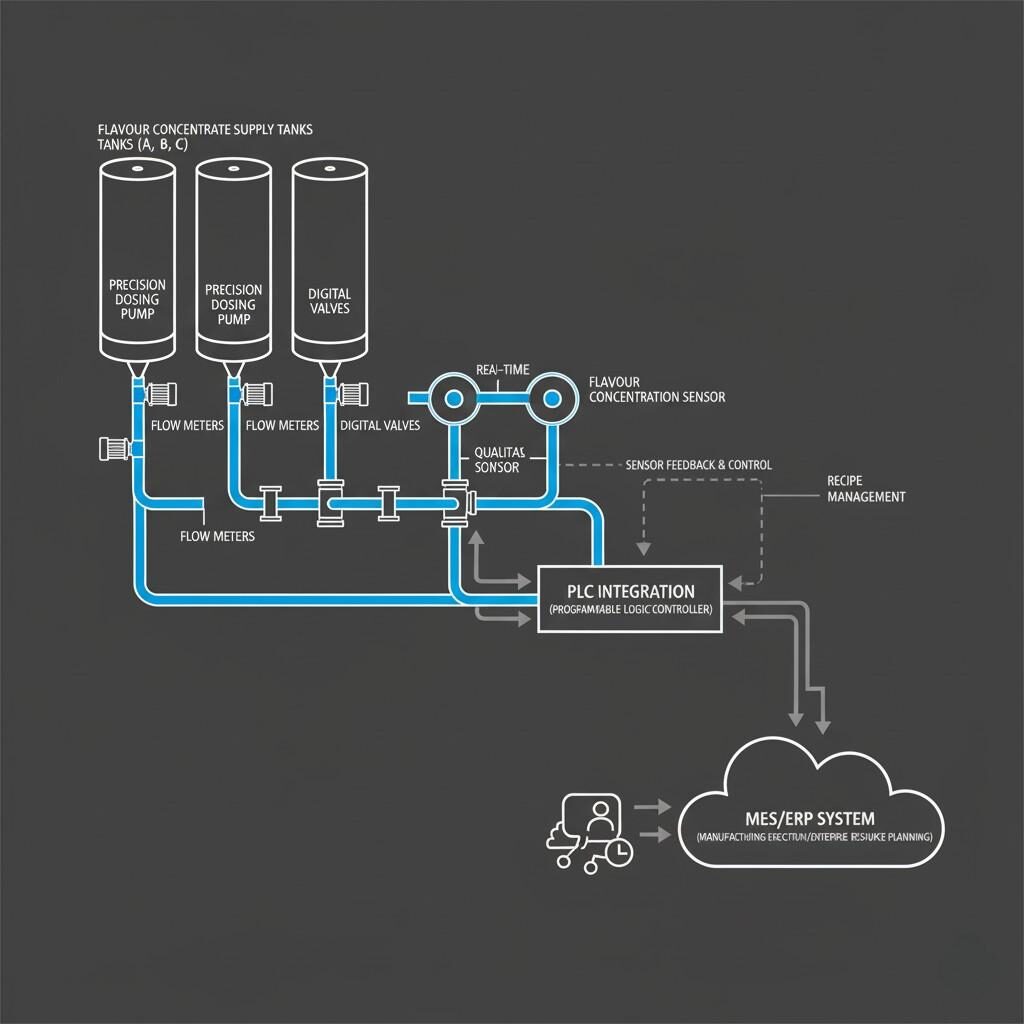
Flavor Dosing Automation Schematic
Here are the major technological elements you and your clients should understand and design around in flavour application automation:
At the heart of automation is accurate dosing of flavour concentrates. Modern systems utilise volumetric or gravimetric pumps, flow meters, digital valves, and feedback loops to ensure the exact required quantity of concentrate is injected into the food/ beverage matrix. The precision ensures correct flavour strength, consistency, and minimal over-use.
Sensors measure flow, temperature, pressure, and sometimes flavour concentration (via inline spectroscopy or refractive index), enabling corrective action if deviation is detected. This feedback ensures each batch meets target specifications.
Automation systems must be integrated with upstream/downstream processes: raw-material handling, bulk conveyance, mixing, homogenising, filling, packaging. Data from flavour dosing is logged in MES (Manufacturing Execution System) or ERP for traceability, batch genealogy, KPI monitoring (e.g., yield, scrap rate, downtime).
In more advanced applications, robotic arms may handle concentrate bottles, change valves, perform CIP (clean-in-place) tasks, and assist flavour switching. Automated Material Handling (AMRs) support such tasks. For example, one study states automation in the food industry via AMRs supports internal logistics and flexible material flows.
Beyond hardware, software layers provide optimisation of dosing parameters, predictive maintenance of pumps/valves, monitoring of performance trends, and adaptation to process variation. For example, a recent review observed that “automation technology can make the production line more intelligent… enabling real-time monitoring and control of temperature, pressure, humidity, and other parameters.”
In flavour application, hygiene and cross-flavour contamination risk are critical. Automated change-over systems, CIP loops, and sanitisation routines must be built in. Automation enables rapid flavour change-over with minimal downtime and minimal manual cleaning.
Every flavour addition should be logged: concentrate batch number, dosage, time-stamp, line ID, operator ID (if applicable), and integration with quality control. This traceability supports quality assurance, regulatory compliance and potential recall requirements. Automation ensures minimal manual entry and error risk.
These components form the technology stack for automated flavour application. In the next sections we explore how this stack delivers benefits, what trade-offs exist, and how to implement effectively.
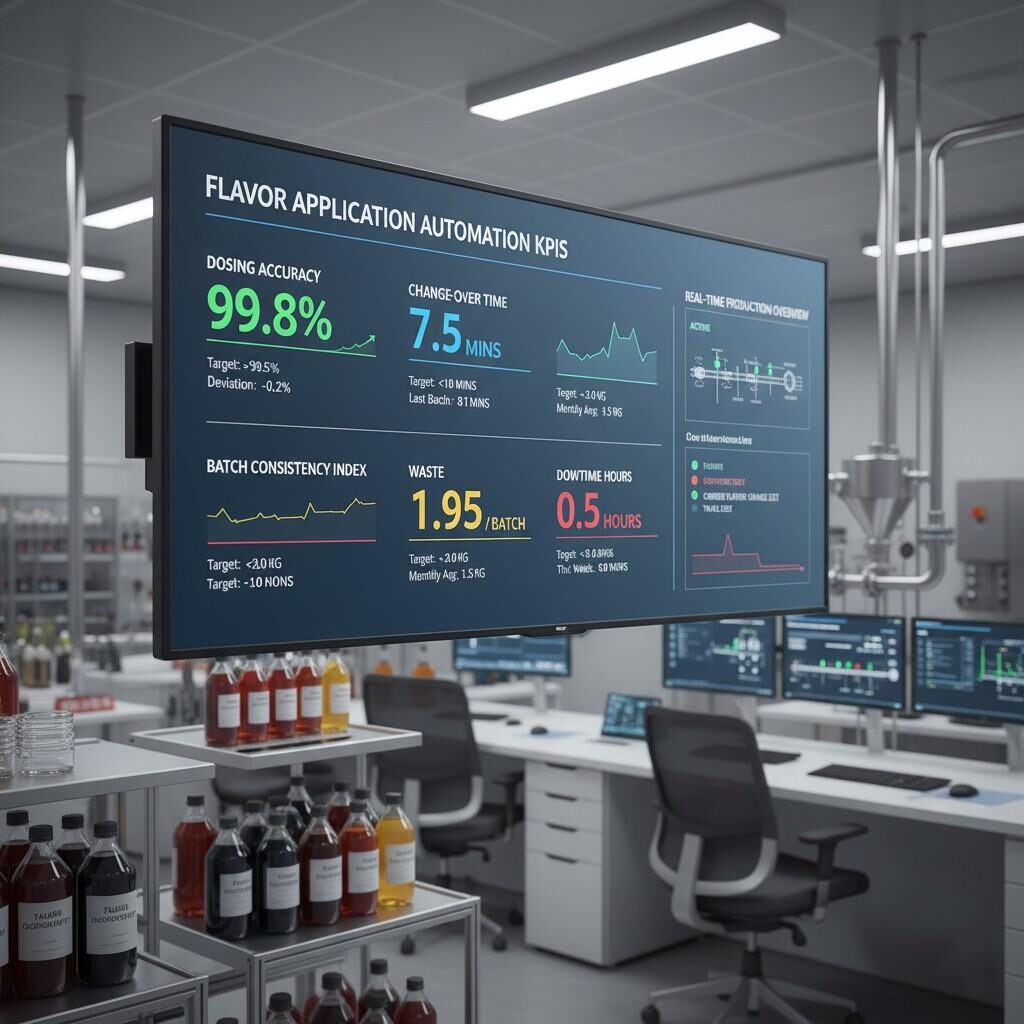
Flavor Automation KPI Dashboard
Automation ensures each batch receives the exact required aroma concentrate dosage and consistent injection timing and mixing. One benefit article notes: “An automation system produces predictable, consistent results. … That is essential when you’re working in the food and beverage industry.”
For a flavour manufacturer, this means you can guarantee the performance of your aroma modules across multiple customer sites and reduce risk of flavour variation or deviation.
Automated flavour application lines can operate faster, with shorter change-overs, fewer manual steps and longer uptime. A survey found 70 % of food & beverage manufacturers cited productivity as the primary benefit of automation.
Metrics to monitor:
Manual dosing often leads to over-dosing, mis-injection, or scrap due to off-spec flavour strength. Automation helps reduce such waste. One case: a dairy powder producer reduced rework by switching to automated batching.
Savings include:
Automated logging of flavour dosing enables full batch genealogy, supporting quality audits, recalls, and brand protection. Traceability improves compliance and consumer trust.
Automation enables flavour houses and food & beverage companies to switch quickly between flavour systems or variants, reducing time-to-market for new product launches. Smart manufacturing platforms help respond to consumer trends and flavour innovations.
Automated flavour application is a stepping stone toward overall digital transformation: integration with Industry 4.0, data analytics, predictive maintenance, and continuous improvement. It positions your factory for future capability rather than one-off manual assembly.
While the capital cost of automation is non-trivial (pumps, sensors, robotics, control systems), the payback period can be shortened by focusing on:
Your role as a flavour manufacturer: you can support customers by providing pre-configured flavour application modules (hardware + software), training, and integration guidance to accelerate ROI.
Automation brings significant benefits, but also requires careful planning. Here are key challenges and how your organisation can address them.
Automation systems often require significant up-front capital: metering pumps, valves, sensors, robotics, PLC/SCADA systems. ROI may be delayed if utilisation is low or system is not designed well. Mitigation: develop modular flavour application systems, build business case with flavour manufacturers (show concentrate cost savings, waste reduction, throughput gain), offer pilot programs or phased implementation.
Flavour application automation must integrate into existing production lines (mixers, fillers, conveyors) and into ERP/MES systems. Poor integration may result in islands of automation, data silos, or bottlenecks. Mitigation: design flavour-application automation with open architecture, use standard communication protocols (OPC UA, MQTT), ensure data logging designed from day-one.
Flavour application isn’t simply “pour this concentrate”. The matrix (liquid, powder, beverage, batch size), the rheology (viscosity), the mixing time, temperature, and the flavour concentrate characteristics all affect dosing and mixing. If automation ignores these, dosing may be inaccurate or mixing incomplete. Mitigation: your flavour-house must supply characterisation data (viscosity, temperature sensitivity, solubility) of each aroma module and support commissioning of dosing systems.
Changing from one flavour system to another (especially when colours/aromas differ) demands cleaning and sanitation. Automated change-over systems must address flavour carry-over, CIP cycles, sanitisation verification. If not, there is a risk of cross-flavour contamination, quality deviation or regulatory non-compliance. Mitigation: design change-over protocols, provide cleaning recipes, support automation of CIP loops and integrate sensors for rinse verification.
Automation requires staff with new skills (maintenance of pumps/valves, PLC programming, sensor calibration, data analytics). Without training, automation can be under-utilised or breakdowns prolong downtime. Mitigation: flavour manufacturer can provide training modules for clients, build operator manuals specific to flavour-application automation, and support remote troubleshooting.
Frequent flavour variant changes (many SKUs) challenge automation systems: each flavour may require different dosing parameters, mixing recipes, switching supply lines. Without proper change-over management, automation may become a bottleneck. Mitigation: develop modular supply systems, colour-coded lines, recipe management software, set up flavour-module standardisation.
Automation generates rich data—but many companies struggle to convert data into actionable insights. Without analysis, sensor logs sit unused and the promise of “smart flavour application” is under-delivered. Mitigation: your flavour-manufacturer can partner with clients to provide dashboards, KPI templates (e.g., dosage deviation, batch yield, waste rate), and analytics best-practice.
By proactively addressing these challenges, your company will not only supply aroma concentrates but will become a trusted partner in flavour-application automation, supporting your clients to scale, innovate and maintain consistency.
Here is a step-by-step workflow for your organisation to enable and support automation in flavour application for your clients.
By following this roadmap, your company elevates from aroma-module supplier to technical partner in automated flavour application—a strong competitive differentiator.
As a professional manufacturer of food and beverage flavours, your company has a key strategic role in enabling automation across the flavour application value chain. Here are the ways you can lead:
Ensure your aroma systems are automation-ready: supplied in formats compatible with metering systems (standardised containers, consistent viscosity, digital batch-IDs). Provide specification documentation, dosage guidelines, and automation integration guidance.
Offer your clients (food & beverage manufacturers) a service package: training for operators and maintenance staff, commissioning support for the dosing subsystem, calibration services, and data-analytics dashboards. This support enhances your value proposition and deepens client relationships.
Partner with automation equipment vendors to develop turn-key flavour application modules: dosing subsystem + PLC/SCADA + recipe management + data logging. Position your company as a co-developer of automation solutions within the flavour application domain.
Embed traceability into your flavour modules: digital batch IDs, bar-codes, QR codes, IoT sensors if applicable. Provide clients with data sheets that integrate with MES/ERP flavour application logs.
Automated flavour application allows quick rollout of new flavour systems. Your company should leverage this agility: design flavour modules with parametric dosing for automation, test concentrated variants optimized for metering pumps, provide sample kits for trial automation lines.
Use automation-readiness as a marketing differentiator: “Our aroma systems are formulated for high-precision dosing and automated production lines,” “Support for flavour application automation and traceability,” “Reduced waste and consistent flavour profile delivered via automated dosing.”
By fulfilling these roles, your company positions itself as a leader in the intersection of flavour manufacturing and automation—a compelling proposition for F&B customers aiming for Industry 4.0 readiness.
Automation in flavour application is not a future concept—it is a present necessity. For flavour manufacturers and food & beverage producers alike, the ability to dose aroma concentrates with precision, traceability, efficiency and scalability will become a core competitive advantage. As we have explored:
As your company positions itself in this dynamic environment, you have a unique opportunity: to offer not just aroma concentrates, but automation-enabled flavour solutions that help your clients succeed in high-speed, high-quality production. In doing so, you increase your value, deepen partnership, and differentiate in a crowded flavour market.
We invite you and your R&D/operations teams to explore how automation can transform your flavour application process—and how we at [Your Company Name] can assist you.

Automated Flavor Line CTA
If you’re ready to explore automation-enabled flavour application—from precision dosing modules to data-enabled traceability and optimized aroma systems—please contact us for a technical exchange and request a free flavour-application sample kit. Let’s work together to boost your production efficiency, maintain flavour quality at scale, and position your brand for the future of food and beverage manufacturing.
💬 Whatsapp:[+86 189 2926 7983]
📩 email:[info@cuiguai.com]
📞 Tel:[+86 189 2926 7983]
Copyright © 2025 Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.