Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Oct 16, 2025
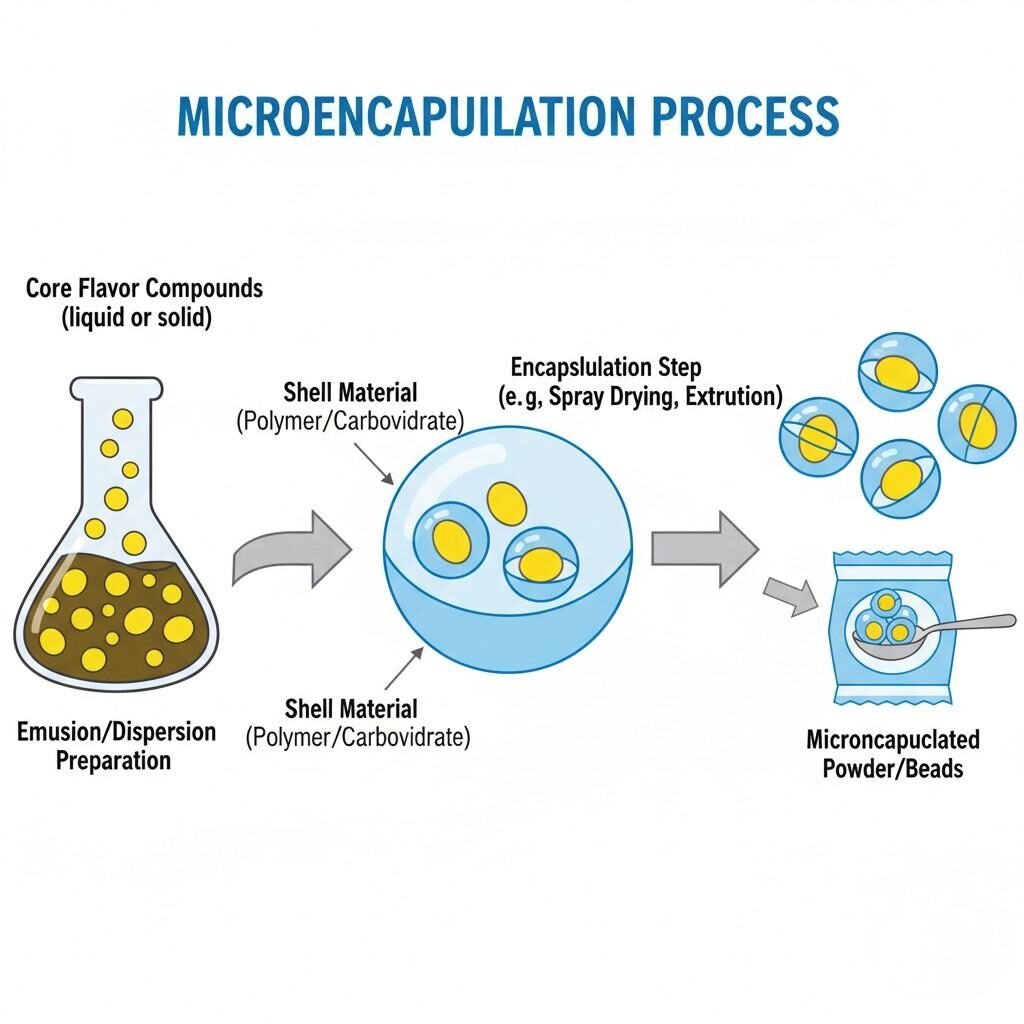
Microencapsulation Process Diagram
In today’s global food and beverage industry, flavor quality defines consumer loyalty. Yet, one of the persistent challenges faced by manufacturers is maintaining flavor stability during processing, storage, and consumption. Volatile aroma compounds—responsible for the characteristic taste and smell—are prone to oxidation, evaporation, or degradation under heat, moisture, or light exposure. To address this issue, microencapsulation technology has emerged as a revolutionary solution.
Microencapsulation involves enclosing flavor molecules within a protective shell, allowing controlled release under specific conditions. The technology not only preserves delicate compounds during manufacturing and storage but also enables targeted flavor delivery—ensuring consistent sensory experiences in the final product.
From powdered drink mixes to baked goods and instant beverages, microencapsulation is redefining how flavor stability and performance are engineered across industries. This article explores the science, materials, techniques, benefits, and industrial applications of microencapsulation, highlighting its crucial role in flavor design and formulation for food and beverage innovation.
Before exploring encapsulation solutions, it’s essential to understand why flavors degrade. Most flavor systems consist of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as esters, aldehydes, terpenes, and alcohols. These molecules are sensitive to:
According to research published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), flavor degradation can lead to up to 40% aroma loss during spray drying or storage if not properly stabilized.
To overcome these challenges, scientists turned to microencapsulation—an approach that mimics nature’s way of protection (e.g., essential oils within plant glands) by physically shielding flavor molecules until they are released during consumption or rehydration.
Microencapsulation is a process of entrapping active compounds within tiny capsules ranging from 1 to 1000 micrometers in size. Each microcapsule consists of two key components:
The encapsulant serves as a barrier to oxygen, light, and moisture, while also allowing controlled release triggered by heat, pH, or mechanical rupture.
The result is a stable, free-flowing powder or bead that retains aroma integrity over long periods. When rehydrated (e.g., during beverage preparation or cooking), the capsule releases the encapsulated flavor, delivering a burst of freshness as if the flavor were newly added.
Selecting the right encapsulating material is critical. Ideal wall materials should have excellent film-forming ability, low permeability to oxygen, and compatibility with flavor molecules.
| Encapsulant Type | Examples | Advantages | Applications |
| Carbohydrates | Maltodextrin, gum arabic, starch, cyclodextrin | Excellent solubility, low cost | Beverages, instant coffee |
| Proteins | Gelatin, casein, whey protein isolate | Controlled release, film-forming | Dairy products, confections |
| Lipids | Hydrogenated oils, waxes | Thermal protection, hydrophobicity | Baked goods, dry soups |
| Polymers | Ethyl cellulose, alginate, chitosan | Precise control over release kinetics | Functional foods, pharmaceuticals |
For flavor applications, gum arabic and maltodextrin remain industry standards due to their excellent emulsifying and drying properties. Recent innovations, however, focus on biopolymer hybrids and nanoencapsulation systems, offering better control and efficiency.
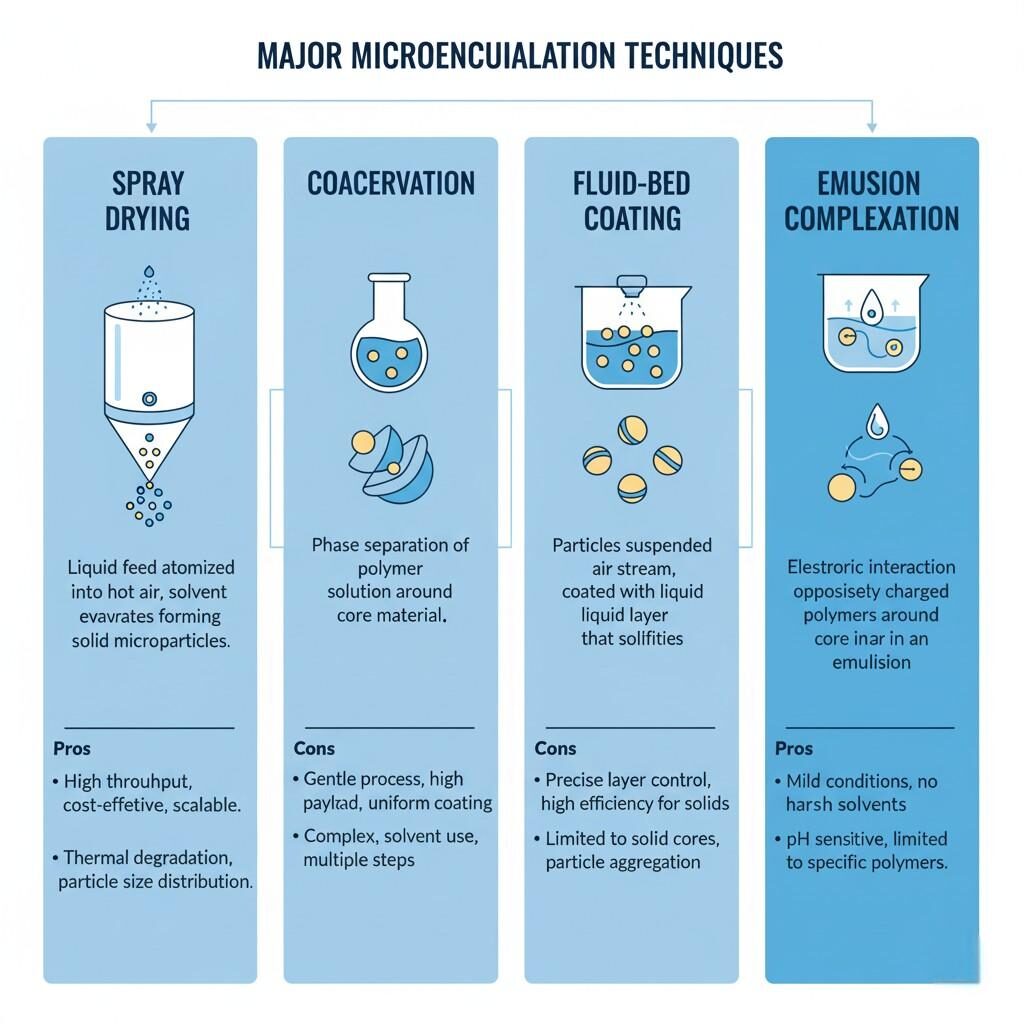
Microencapsulation Techniques Flowchart
The method used determines capsule structure, particle size, and release characteristics. Common techniques include:
The most widely used and cost-effective technique in the food industry.
A flavor emulsion is atomized into a hot air stream, causing rapid water evaporation and formation of dry microcapsules.
Involves phase separation of a polymer solution to form a coating around flavor droplets. Commonly used with gelatin or gum arabic.
Fine flavor particles are suspended in an air stream and sprayed with coating materials (e.g., starch or wax).
Cyclodextrins form molecular cages that trap small flavor molecules through host–guest interactions.
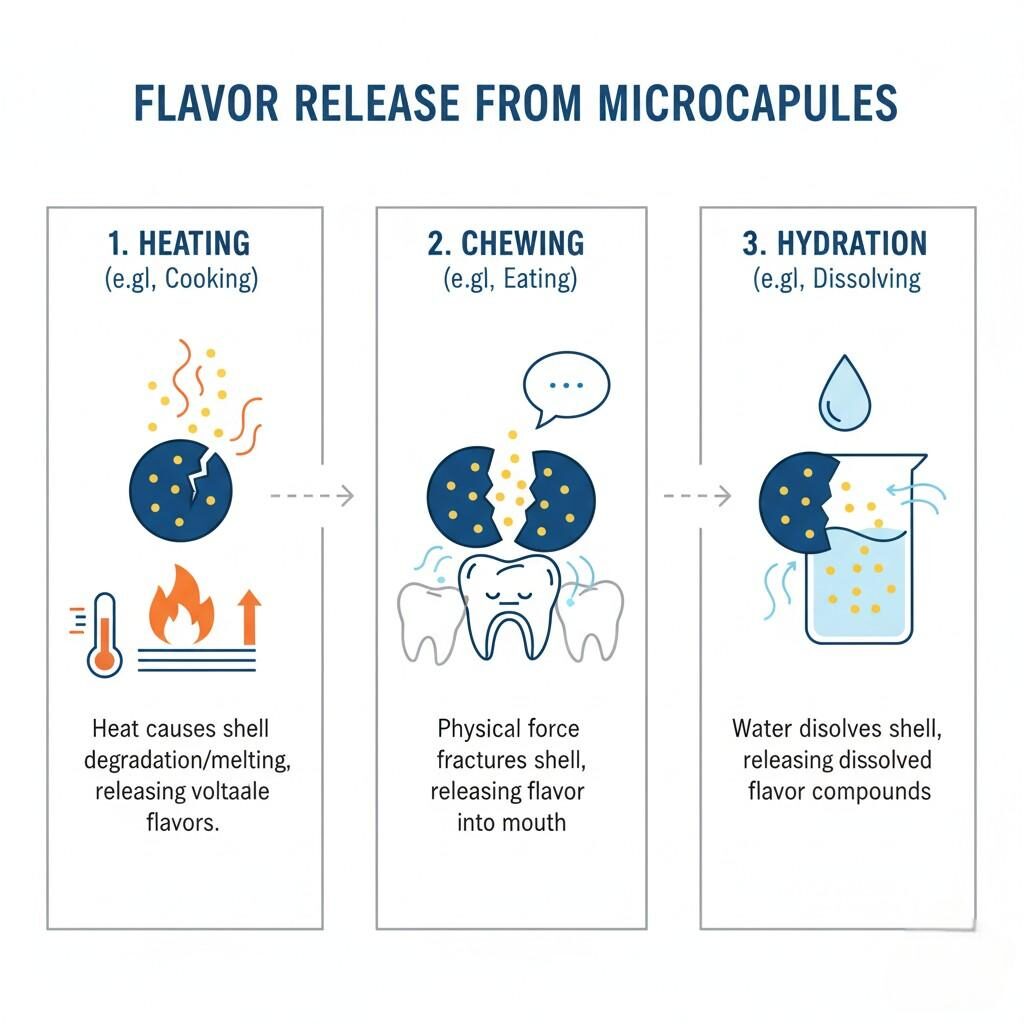
Flavor Release from Microcapsules
The release of encapsulated flavors can be tailored to suit different applications. Mechanisms include:
By controlling wall material composition and capsule morphology, formulators can achieve precise sensory timing—ensuring the right flavor intensity at the right moment.
Microencapsulation offers numerous functional advantages for flavor manufacturers and food processors:
Encapsulated flavors are shielded from oxygen, slowing oxidation reactions that cause off-notes or rancidity.
Encapsulation reduces loss of volatile compounds during spray drying, baking, or extrusion.
Dry encapsulated powders prevent flavor migration in hygroscopic systems like instant soups or dry mixes.
Flavor is released under specific environmental triggers—ensuring freshness during consumption.
Encapsulation enables easy incorporation into both aqueous and lipid-based systems without separation.
According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports, controlled-release technologies like microencapsulation improve flavor retention by up to 60% in high-temperature processes and significantly extend shelf life in dry storage applications (FAO Technical Paper 2019).
Microencapsulation technology is now central to flavor engineering across industries:
| Industry | Example Applications |
| Beverages | Instant coffee, flavored powders, energy drinks |
| Bakery | Cakes, cookies, muffins (heat-activated flavor release) |
| Confectionery | Chewing gum, candies (chew-triggered release) |
| Dairy | Yogurts, flavored milks, frozen desserts |
| Nutraceuticals | Functional powders, fortified snacks |
| Foodservice | Seasoning blends, sauces, soups |
In beverages, for instance, encapsulated citrus oils or natural fruit essences maintain aroma freshness throughout shelf life. In bakery applications, encapsulated vanilla or butter flavors activate during baking, enhancing sensory quality and product differentiation.
As consumer demand shifts toward clean-label and natural flavoring systems, microencapsulation is evolving to align with sustainability and transparency goals.
Researchers are exploring plant-based encapsulants such as pea protein, rice starch, or pectin to replace synthetic polymers.
Advanced techniques at the nanoscale enhance bioavailability and improve flavor solubility in complex systems.
Responsive materials that react to pH changes, temperature, or enzymatic triggers are being developed for precision flavor delivery.
New solvent-free and low-energy encapsulation processes are reducing carbon footprints while maintaining performance.
A recent study published in the Journal of Food Engineering (Elsevier, 2024) highlights that combining nanoemulsion pre-treatment with spray drying can increase flavor retention by over 70% compared to conventional methods—marking a major step toward high-efficiency encapsulation systems.
Despite its many advantages, microencapsulation faces several technical and regulatory challenges:
Looking forward, the integration of AI-assisted flavor modeling, 3D microcapsule printing, and bio-based encapsulants is expected to reshape the future of flavor formulation.
According to a 2024 market report by Grand View Research, the global microencapsulation market for food applications is projected to exceed USD 14 billion by 2030, driven by demand for functional, stable, and premium sensory products.
Microencapsulation represents a perfect intersection of food science, materials engineering, and sensory design. It offers manufacturers a versatile toolkit for preserving, protecting, and releasing flavors with unprecedented precision.
As consumer expectations evolve toward more consistent, natural, and enjoyable flavor experiences, adopting microencapsulation technology will not only enhance product stability but also strengthen brand differentiation and market trust.

Microencapsulated Flavor in Foods
At CUIGUAI Flavoring, we specialize in advanced food and beverage flavor solutions that integrate cutting-edge technologies such as microencapsulation and controlled release systems. Our R&D team focuses on improving flavor stability, solubility, and sensory impact, helping global manufacturers deliver superior product performance.
Whether you are developing new products or improving existing formulations, our technical experts can assist with customized flavor encapsulation strategies tailored to your production environment.
Explore how CUIGUAI’s encapsulated flavors can enhance your products’ aroma performance and shelf stability.
👉 Contact our technical team today for a consultation or free sample.
📩 [info@cuiguai.com]
📞 [+86 189 2926 7983]
🌐 Explore more at 【www.cuiguai.cn】
Copyright © 2025 Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.