Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Nov 17, 2025

Sensory Evaluation Lab
Taste is far more than a biological response — it is a psychological, emotional, cultural, and multisensory experience. When consumers choose a beverage, snack, dairy product, or confectionery item, they are not only responding to chemical stimuli on the tongue. They are processing a complex combination of flavor expectations, memory associations, visual cues, aromas, textures, and even brand trust.
As a professional manufacturer of food and beverage flavorings, CUIGUAI Flavoring works closely with R&D teams to design flavors that align with consumer psychology, creating products that not only taste good but also feel right, look right, and signal the right emotional or functional value.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the science and psychology of taste, diving into the mechanisms that shape consumer perception and influence real-world decisions. By understanding how flavor design aligns with cognitive processes, brands can build stronger loyalty, improve formulation precision, and create emotionally resonant product experiences.
Flavor begins with taste receptors located on the tongue, which detect five primary sensations:
These sensations work together with smell, texture, and visual cues to form what we commonly call flavor.
It is widely documented that 80% or more of flavor perception is derived from smell rather than taste alone. When we chew food, volatile aroma molecules travel to the olfactory receptors through the retronasal pathway, triggering strong emotional memories.
According to the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the olfactory bulb is directly connected to the amygdala and hippocampus, regions responsible for emotion and memory formation — which explains why flavors often evoke nostalgia or emotional responses (NIH, U.S. National Library of Medicine)【citation 1】.
This biological connection forms the foundation of emotional flavor branding, where certain flavor notes (e.g., vanilla for comfort, citrus for freshness) strategically trigger psychological reactions.
Humans have instinctive preferences for certain tastes:
Universities such as Harvard have published research showing that taste preferences are partly genetically inherited but also influenced by early childhood exposure and environmental conditioning (Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health)【citation 2】.
This highlights why flavor manufacturers must consider age demographics and cultural familiarity when designing flavors.
While biology initiates taste, psychology determines interpretation. Two people can taste the same food but report completely different experiences based on:
Here is how each factor shapes perception.
What a consumer expects will strongly influence what they perceive. This phenomenon is known as top-down cognitive processing.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Consumer Research found that when people are told a wine is expensive, they rate it as tasting significantly better—even when the wine is identical【citation 3】.
This same principle applies to flavors:
Expectation dramatically alters the sensory evaluation outcome.
Flavor manufacturers use this knowledge to build narrative-driven flavor solutions that align with desired product positioning.
Flavor memory is incredibly durable. One childhood taste can become a lifelong preference—or aversion.
The olfactory memory system is so powerful that even decades-old aroma memories can be recalled instantly — a phenomenon documented widely in neuroscience research (e.g., MIT’s Picower Institute for Learning and Memory)【citation 4】.
Brands capitalize on this by using flavors that generate:
Flavors create emotional identity.
Flavor psychology extends beyond the tongue:
People associate certain colors with expected flavors:
If the color doesn’t match the expected flavor, satisfaction drops—even when the formula is unchanged.
Crisp sound = freshness.
Research shows that consumers perceive potato chips as fresher when the crunch is louder.
Creaminess enhances perceived sweetness, while effervescence enhances citrus notes.
In flavor design, understanding these multisensory interactions helps create holistic consumer experiences.
Flavor is deeply cultural. What is considered delicious in one region may be strange in another. Understanding cultural context is essential for global food and beverage brands.
The more often a flavor is encountered during childhood, the more likely it becomes a lifelong preference. This concept is known as the familiarity principle or the mere exposure effect.
Flavor manufacturers designing products for regional markets must therefore understand:
This ensures flavor launches align with market readiness.
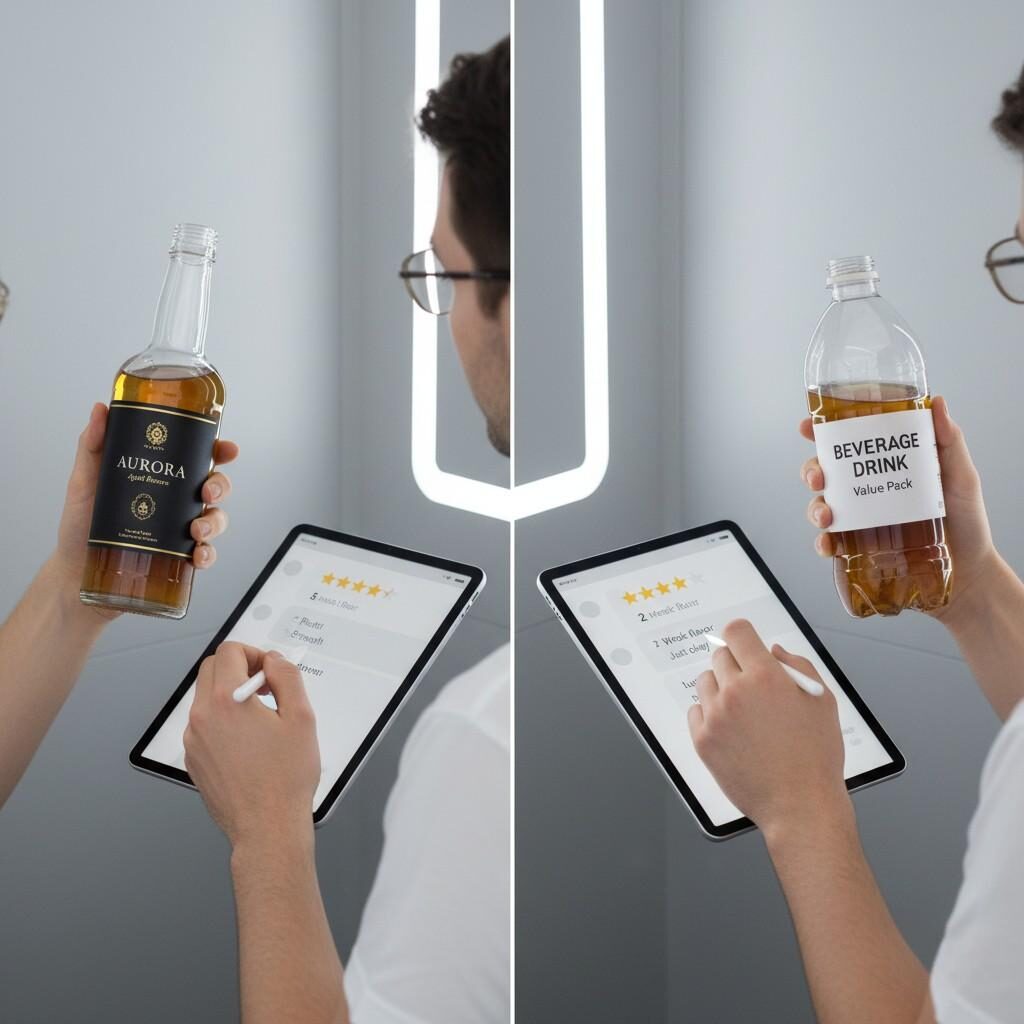

Packaging Impact Comparison
Marketing influences flavor perception long before the product is tasted.
Premium packaging increases perceived flavor quality—even if the formula remains identical.
Words like “slow-steeped,” “sun-ripened,” or “artisan” create psychological value that amplifies taste.
Consumers prefer flavors with stories:
Storytelling increases flavor resonance and brand loyalty.
Labels such as “low sugar,” “natural flavor,” or “vitamin-enriched” change how sweetness or bitterness is perceived. Because consumers associate health attributes with altered taste, formulators often adjust sweetness, acidity, and aromatics to match perception.
Flavor is the #1 repeat-purchase driver in food and beverages. Not price. Not packaging. Not marketing.
Here are the most influential psychological factors affecting consumer choice:
Consumers choose flavors based on emotional state:
Consumers balance new experiences (“limited editions”) with comfort flavors (“classic vanilla”). The key is controlled novelty—new but not too unfamiliar.
Lifestyle segmentation (athletes, professionals, parents, students) influences flavor expectations even more than gender.
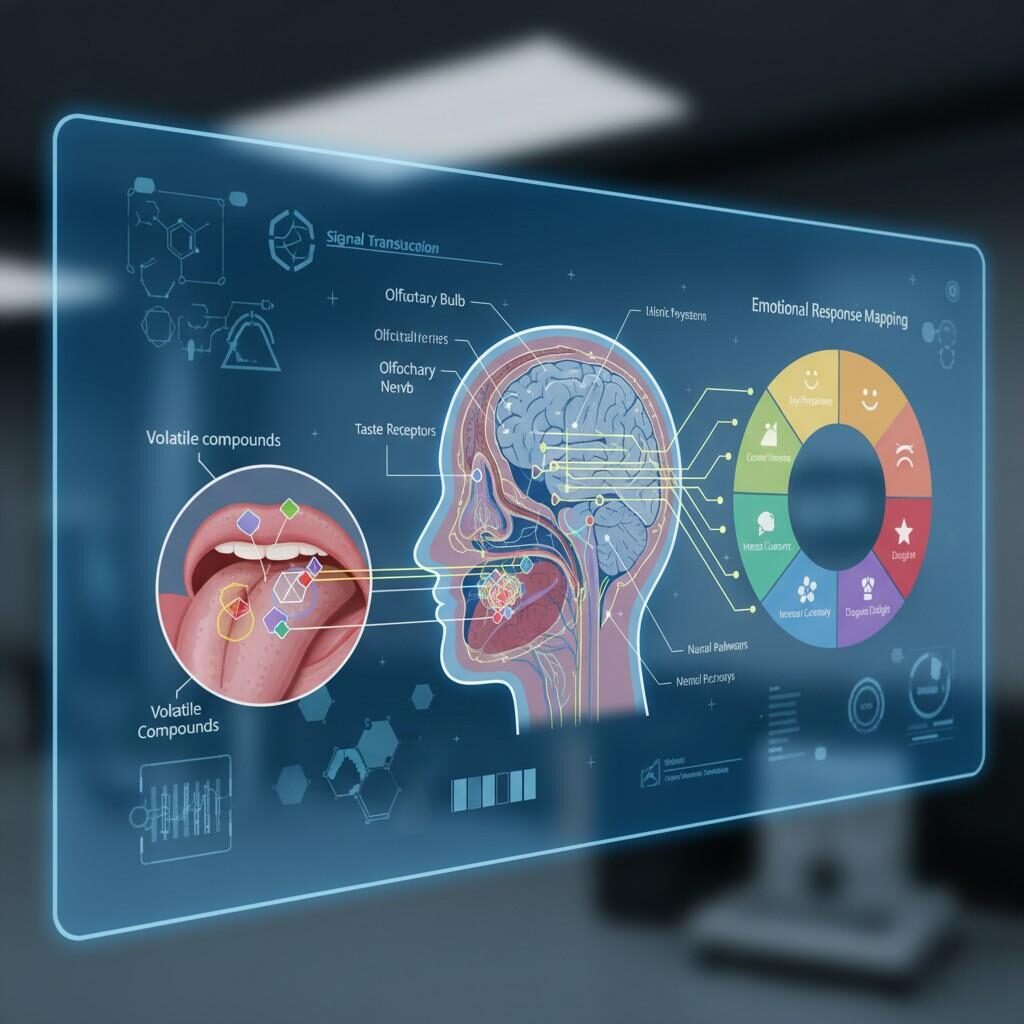
Neuro-Sensory Flavor Mapping
Flavor R&D requires mastery of both chemistry and psychology.
Professional sensory panels evaluate:
Consumer testing validates whether the flavor works in real-world psychological conditions.
This emerging field studies how specific flavor compounds activate neural pathways associated with:
Flavor creation guided by neurosensory insights achieves higher consumer acceptance.
Driven by global stress and desire for emotional reassurance.
Linked to wellness and hydration trends.
Associated with sophistication, mindfulness, and premiumization.
Driven by Gen Z and social media curiosity.
Aromatics help compensate for reduced sweetness perception.
Flavor manufacturers can strategically build portfolios based on these psychological drivers.
A beverage client wanted to create a “functional relaxation drink.”
Traditional botanical flavors tasted too herbal for mainstream consumers.
AI models analyze global consumer sentiment and sensory data to predict preference trends.
Future flavors may be designed to trigger targeted neural pathways—e.g., focus-enhancing citrus or calming herbal profiles.
With wearable technology and diet customization, flavors may adapt to:
Flavor psychology will become even more precise and impactful.

Flavor Design & Brand Trust
Flavor is not simply a taste — it is an emotion, a memory, a cultural signal, and a decision driver. Companies that understand the psychology of taste can create products that resonate deeply with consumers, leading to stronger loyalty, longer shelf presence, and more powerful brand stories.
At CUIGUAI Flavoring, we integrate scientific research, sensory psychology, and formulation expertise to help brands develop flavor solutions that truly influence consumer perception and choice.
If you are developing a new food or beverage product and want flavor solutions backed by sensory psychology, scientific formulation, and market insights, our R&D team is ready to assist.
👉 Contact us for technical consultation or request free flavor samples today.
📧 Email: [info@cuiguai.com]
🌐 Website: [www.cuiguai.cn]
📱 WhatsApp: [+86 189 2926 7983]
☎ Phone: [+86 0769 8838 0789]
Let’s co-create the next consumer-loved flavor innovation.
Copyright © 2025 Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.