Author: R&D Team, CUIGUAI Flavoring
Published by: Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd.
Last Updated: Oct 27, 2025
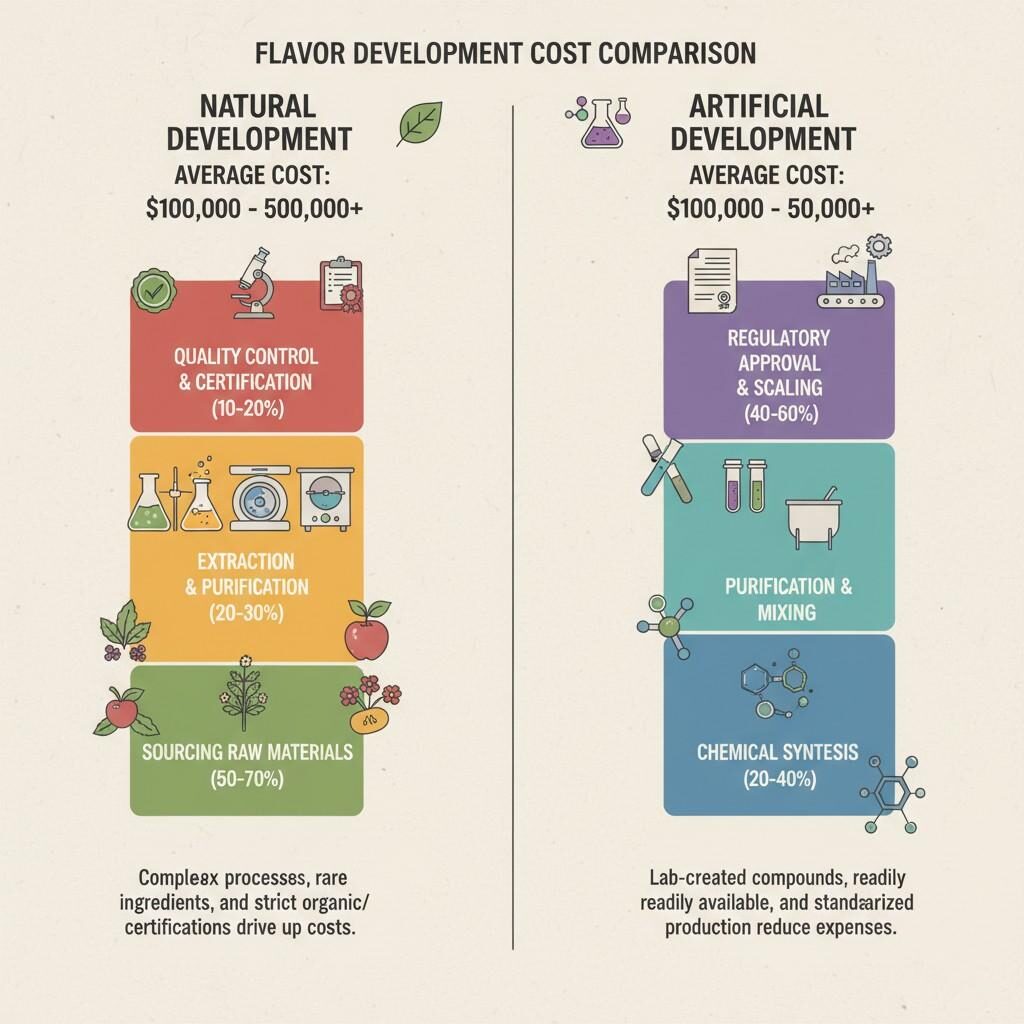
Flavor Development Cost Comparison
In the modern food and beverage industry, flavor drives consumer perception, brand identity, and market success. Yet behind every taste experience lies a precise balance between art, science, and economics. For manufacturers, the challenge is no longer just creating great-tasting products—it’s about delivering that taste at scale and at cost.
A flavor that performs perfectly in a lab may not survive commercialization if its formulation cost is too high or its raw materials fluctuate in price. This is where flavor cost analysis becomes essential. It’s not simply an accounting exercise—it’s a systematic method to identify how every ingredient, process, and decision contributes to both sensory quality and profitability.
Flavor cost analysis involves evaluating:
When all these elements are optimized, manufacturers can achieve a critical outcome: maximum value without compromising sensory quality.
The cost of flavor is often hidden beneath layers of formulation complexity. While the ingredient cost may seem like the main driver, it’s only part of a broader system that includes formulation efficiency, process design, compliance, and logistics.
| Cost Component | Description | Influence on Quality and Value |
| Raw Materials | Natural extracts, essential oils, synthetic aroma compounds | Core to authenticity and stability |
| Formulation Complexity | Solubility, masking, and stability adjustments | Impacts performance and consistency |
| Processing Technology | Encapsulation, emulsion systems, drying methods | Affects yield, stability, and flavor release |
| Regulatory Compliance | Labeling, GRAS status, certifications | Essential for legal and consumer trust |
| Supply Chain & Storage | Logistics, climate impact, seasonality | Determines continuity and cost predictability |
Understanding these interdependencies enables more accurate cost modeling and better decision-making.
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), all flavoring substances must meet purity and safety criteria before use in foods, which directly influences sourcing strategies and production complexity (Source: FDA.gov). Compliance isn’t optional—it’s a fixed cost of doing responsible business.
The choice between natural and artificial flavors remains a key cost determinant. Natural flavors, derived from plants, fruits, or animal sources, typically involve complex extraction and purification steps. Their prices depend on agricultural yields, geopolitical stability, and labor costs. Artificial or nature-identical flavors, on the other hand, are produced via controlled synthesis, resulting in predictable costs and consistent quality.
| Flavor Type | Typical Cost Range (per kg) | Advantages | Challenges |
| Natural | $60–$300+ | Authentic sensory profile, clean-label appeal | Price volatility, supply limitations |
| Artificial | $15–$80 | Cost-effective, reproducible, scalable | Consumer skepticism, label restrictions |
| Hybrid | $40–$150 | Balanced cost-performance ratio | Requires expert formulation |
Many global manufacturers now adopt hybrid systems—a blend of natural and synthetic molecules designed to mimic premium sensory profiles while maintaining stable pricing. This approach can reduce total flavor cost by 15–25% without affecting consumer acceptance.
Agricultural origin strongly impacts flavor cost. Vanilla sourced from Madagascar, citrus oils from Brazil, or coffee extracts from Ethiopia all fluctuate seasonally. Droughts, natural disasters, or political events can sharply increase prices.
For example, the global vanilla market saw unprecedented volatility in 2017, with prices exceeding $600/kg—up from under $100/kg just a few years earlier. Such swings disrupt entire supply chains.
To mitigate risk:
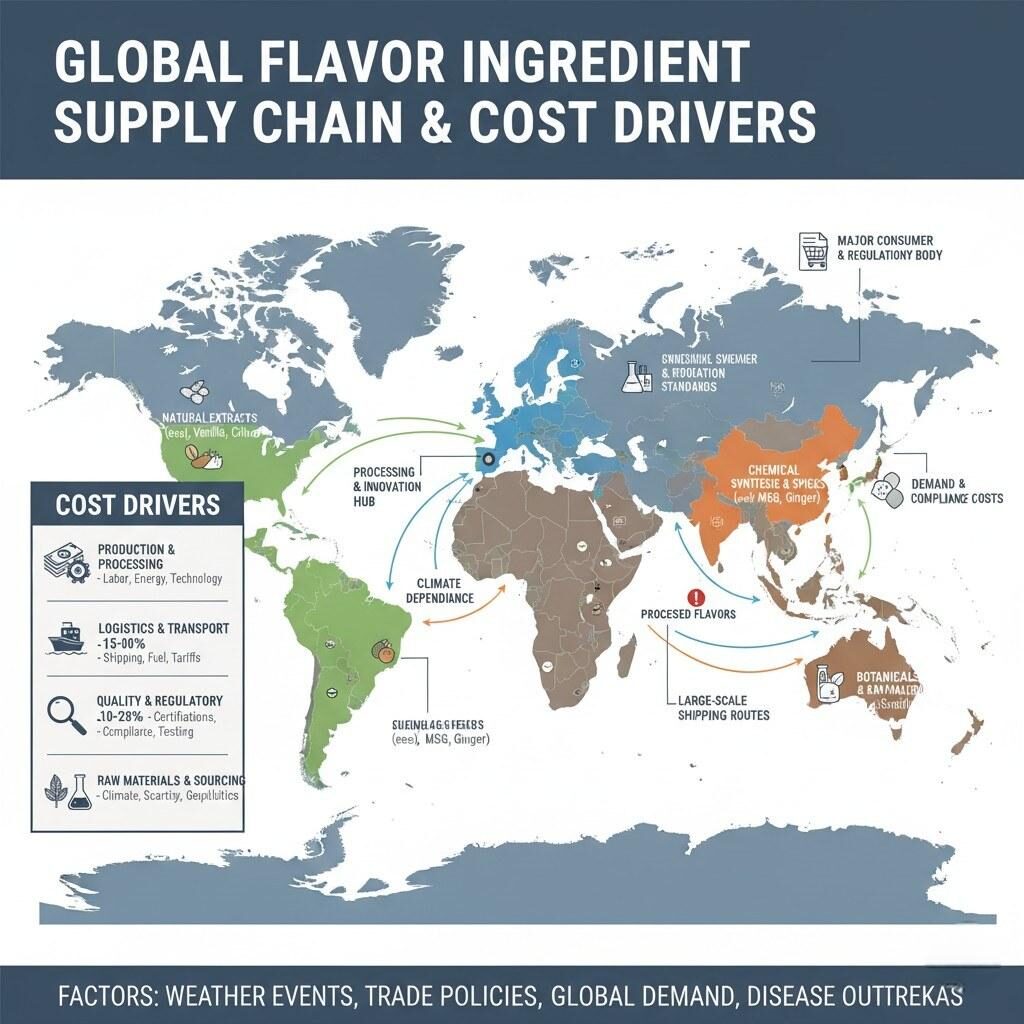
Global Flavor Ingredient Supply Chain
Reformulation is not about cutting corners—it’s about precision engineering. A technically advanced R&D team can reformulate a product to reduce raw material costs without altering the sensory experience. This requires understanding flavor chemistry, solubility, matrix interaction, and thermal stability.
Some strategies include:
A study from the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) reported that encapsulated flavor systems achieved up to 25% ingredient cost savings compared to free oil flavors while maintaining similar sensory acceptance (Source: IFT.org).
The goal of flavor optimization is not necessarily to use less flavor, but to use it more efficiently. High-strength concentrates often offer lower cost-in-use, even if their price per kilogram appears higher. Through controlled dosing systems and pilot trials, manufacturers can find the sweet spot where cost efficiency and sensory intensity intersect.
Encapsulation techniques—such as spray drying, fluid bed coating, or liposomal entrapment—protect delicate aroma molecules from oxidation, light, and heat. These systems extend shelf life and reduce loss during high-temperature applications such as baking or extrusion.
Benefits include:
Although encapsulation increases upfront production cost, the total cost-in-use often decreases by 10–20% due to improved yield.
For liquid and beverage applications, flavor emulsions stabilize oil-based flavor compounds in water systems. Modern nanoemulsions with droplet sizes below 200 nm enhance clarity, mouthfeel, and release. They also allow flavor concentration reduction without perceptible sensory loss.
Production efficiency can also reduce cost through:
The cost-per-kilogram metric can be misleading. What matters is cost-in-use—the actual expense required to achieve the target flavor intensity in the final product.
Example:
Even though Flavor A is more expensive by weight, it delivers better value in use.
Manufacturers should integrate sensory data into cost models. Triangle tests, quantitative descriptive analysis (QDA), and hedonic scaling can correlate perceived intensity with concentration. Statistical modeling (e.g., ANOVA, regression) helps identify optimal inclusion rates that minimize cost while maintaining target perception levels.
Regulatory frameworks define what ingredients can be used, in what quantities, and under what labeling claims. Adhering to these standards incurs analytical testing, documentation, and auditing costs, but ensures market access and brand safety.
Key global frameworks include:
Educational institutions like Cornell University’s Department of Food Science emphasize that transparent labeling and compliance are central to both brand reputation and consumer confidence (Source: Cornell University, Food Science Department).
Comprehensive QA includes:
Investing in these systems early prevents costly reformulation or recalls later.
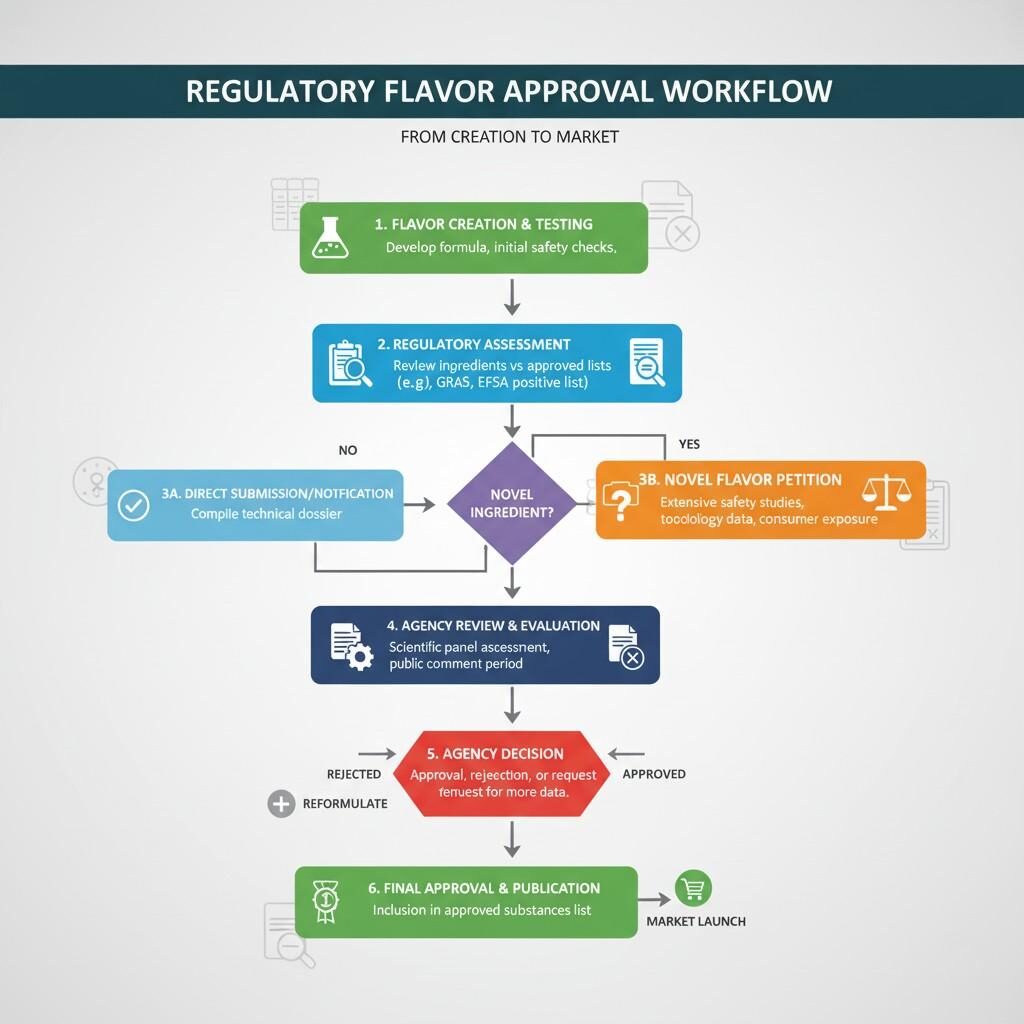
Regulatory Flavor Approval Workflow
Sustainability is no longer a luxury—it’s a stabilizer. Responsible sourcing reduces risk exposure to raw material shortages and consumer backlash.
Benefits of sustainable sourcing:
For instance, Symrise AG has demonstrated that implementing sustainable sourcing for vanilla reduced cost variability by 30%, while boosting traceability and quality consistency (Source: Symrise Official Sustainability Report).
Sustainability also means:
Over time, these investments produce measurable long-term cost stability.
The modern flavor industry is increasingly data-centric. Digital flavor informatics—the integration of chemical data, sensory data, and cost models—enables precise decision-making.
Key tools include:
These tools empower R&D and procurement teams to collaborate efficiently, reduce trial-and-error time, and maintain agility in volatile markets.
Collaborating with a professional flavor manufacturer transforms cost control from a reactive measure to a proactive strategy. An experienced partner contributes:
Through co-development, businesses can access cutting-edge R&D capabilities without maintaining large in-house teams, reducing both cost and time to market.
A ready-to-drink tea manufacturer aimed to lower flavor costs while preserving sensory consistency across production batches.
Challenge:
Citrus top notes were volatile, requiring high loading levels to maintain aroma. Supply fluctuations of natural lemon oil increased cost.
Solution:
Outcome:
This case illustrates how technical innovation and strategic collaboration deliver measurable economic value.
Looking ahead, the next frontier of flavor cost optimization will merge biotechnology, sustainability, and AI. Key trends include:
The convergence of technology, transparency, and taste science will redefine how manufacturers evaluate cost—not just in dollars per kilogram, but in total product value per consumer experience.
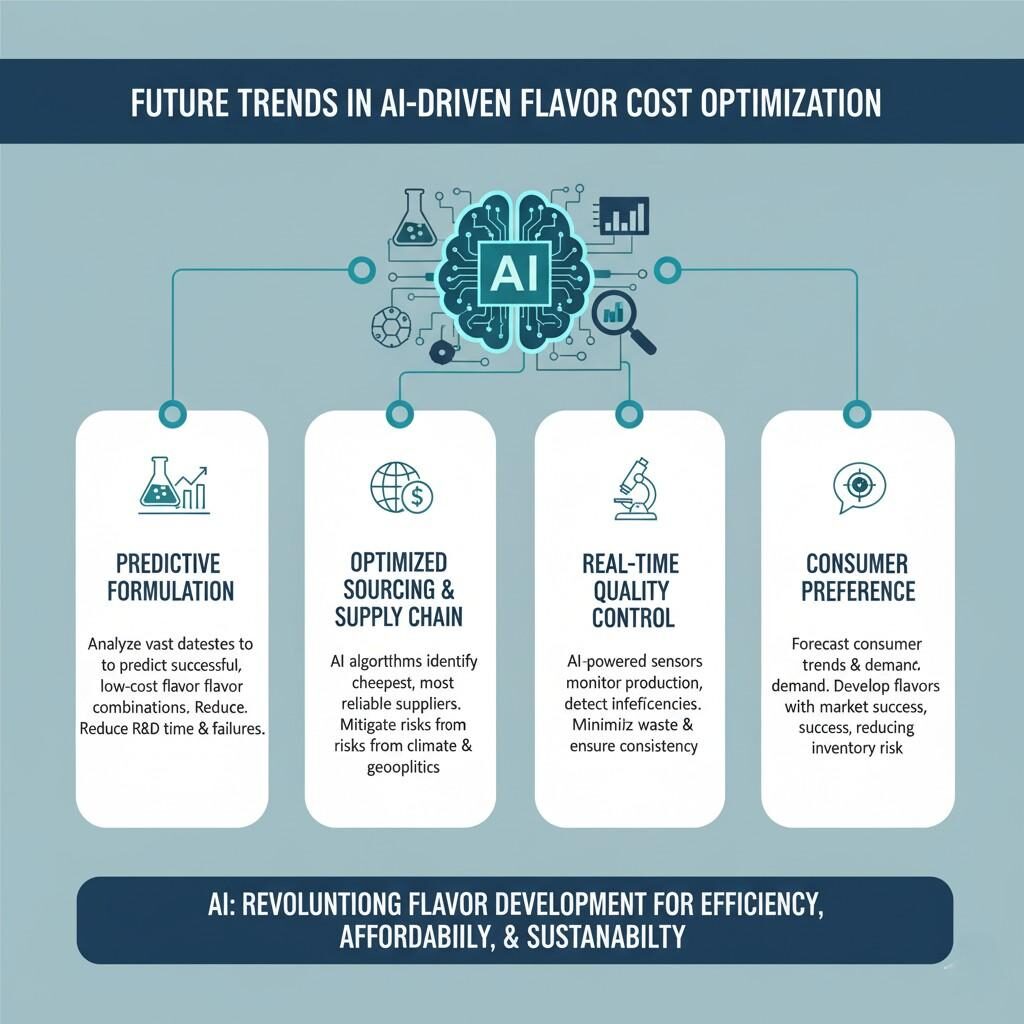
AI in Flavor Cost Optimization
Flavor is both a sensory signature and a strategic investment. When managed scientifically, cost optimization enhances—not diminishes—product quality.
True cost efficiency emerges from aligning formulation science, processing technology, sustainability, and data intelligence under one integrated framework.
The most successful companies will not merely chase lower prices but will build value-engineered flavor systems that deliver consistent quality, supply stability, and market differentiation.
At CUIGUAI Flavoring, we specialize in crafting high-performance, cost-efficient flavor solutions tailored for the food and beverage sector. Our R&D experts apply advanced analytics, encapsulation technology, and global sourcing intelligence to help you maximize flavor value and minimize formulation cost.
👉 Contact us today for a technical consultation or to request free flavor samples.
📩 [info@cuiguai.com]
📞 [+86 189 2926 7983]
🌐 Explore more at 【www.cuiguai.cn】
Copyright © 2025 Guangdong Unique Flavor Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.